RBC Segmentation
Semantic Segmentation on Variable Sized Images of Red Blood Cells using Deconvolution Networks
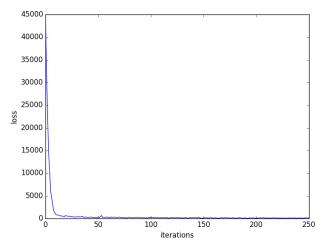
This project focused on the task of semantic segmentation on images of red blood cells. We trained a deconvolution network for this task. The deconvolution network is composed of deconvolution and unpooling layers, which identify pixel-wise class labels and predict segmentation masks. We train the model on various images of red blood cells. We apply the trained model on the test dataset and construct the final semantic segmentation map. We have got 100% results with the intersection over mean (IoU) of the test images of more than 95%. This clearly signifies that the model that we have trained is highly efficient and can be used for any segmentation tasks with just few training iterations.
Architecture
- Each training image is 128 x 128 pixels image.
- We take the input as 128 x 128 x 3 where 3 denotes the channels of RGB image.
- This input is fed to a convolutional layer followed by ReLU layer.
- The output of the previous layer is again fed into a convolutional layer followed by ReLU layer.
- The next layer is max pooling layer with filter size of 2 x 2.
- The above set of layers is repeated three times, making in total of 6 convolutional layers each followed by a ReLU layer, with a max pooling layer at intervals of two.
- The output of the above network is fed into a dropout layer with keep probability of each neuron of 0.5.
- The next layer is an unpooling layer.
- The output of the layer is fed into a deconvolution layer.
- Similarly, the deconvolution network is just the reverse of the convolution network.
- The final output is scaled into height x width x 2 where 2 denotes the two class labels, namely class label and background label.
Experiment setup
The dataset comprises of 164 images of red blood cells each having dimensions of 128 x 128. The entire code is run using TensorFlow 1.0 and is trained on Tesla GPU, which took around 20 minutes for 5-fold cross validation. We did a 5–fold cross validation on the training set using Scikit Learn. We used cross entropy as our loss function. The trained model is tested on the test dataset which comprised 40 variable sized images of RBCs.